Last Updated on February 5, 2026 by admin
Wire transfers are one of the fastest and most secure ways to send money domestically or internationally. To complete a wire transfer through Bank, you’ll need specific details, including the correct routing number.
When managing your finances, especially when setting up direct deposits, paying bills, or transferring money, you’ll often be asked for two key pieces of information: your routing number and your account number. Though they appear together on checks and in online banking, they serve distinct purposes. This article breaks down what each number means, how they work, and why they matter.
Key Takeaways
- A routing number is a nine-digit identifier for U.S. banks.
- It is required for ACH transfers, wire transfers, and check processing.
- Always verify your bank’s routing number before sending money to avoid delays.
- For international transfers, you’ll need both the routing number and SWIFT code.
Read: Factors that determine foreign exchange Rate of a country
What Is a Routing Number?
A routing number (also known as an ABA number or transit number) is a unique nine-digit code assigned to financial institutions in the United States. It acts like a bank’s “address” in the digital payment system, telling other institutions exactly where to send or receive funds.
Routing numbers were first introduced by the American Bankers Association (ABA) in 1910 to streamline check processing. Today, they are essential for electronic transactions such as:
- Direct deposits (payroll, government benefits)
- ACH transfers (bill payments, peer-to-peer transfers)
- Wire transfers (domestic and international)
- Check processing
Structure of a Routing Number
Each routing number is carefully structured to prevent errors:
- First 4 digits: Federal Reserve routing symbol.
- The first 2 digits indicate the Federal Reserve district (out of 12).
- Next 4 digits: Identify the specific financial institution.
- Final digit: A check digit used to verify the number’s validity.
Example: 123456789
- “12” → Federal Reserve district
- “3456” → Bank identifier
- “9” → Check digit
Where to Find Your Routing Number
- On a check: Printed at the bottom left corner in magnetic ink.
- Bank statements: Often listed in account details.
- Online banking/mobile app: Accessible under account information.
- Customer service: You can call your bank to confirm.
Why Routing Numbers Are Important
In today’s digital banking world, money moves faster than ever. Whether you’re setting up direct deposit, paying bills online, or sending a wire transfer, one small detail makes all the difference: the routing number. This nine-digit code ensures your money gets to the right place, safely and efficiently.
1. Accuracy in TransactionsRouting numbers prevent your money from being misdirected. Each bank has its own set of routing numbers, ensuring that funds go exactly where they’re supposed to.
2. Different Transactions, Different Numbers
- ACH transfers: Used for direct deposits, bill payments, and peer-to-peer transfers.
- Wire transfers: Often require a separate routing number or SWIFT code for international payments.
- Checks: Routing numbers printed on checks help banks process them quickly.
3. Security and ReliabilityBecause routing numbers are unique to each institution, they reduce the risk of fraud or errors. They act as a safeguard in the financial system.
4. Regional DifferencesLarge banks may have multiple routing numbers depending on the state or type of transaction. Using the wrong one can delay or even cancel your payment.
Routing Numbers vs. SWIFT Codes
When transferring money, whether domestically or internationally, accuracy is everything. Two key identifiers make this possible: routing numbers and SWIFT codes. While both serve to direct funds to the right financial institution, they operate in different contexts
What Is a Routing Number?A routing number is a nine-digit code used in the United States to identify banks and credit unions. It ensures that money transfers, bill payments, and deposits are directed to the correct institution.
- Scope: Domestic transactions only (within the U.S.)
- Format: 9 digits (e.g., 031101266)
- Uses:
- Direct deposits (payroll, government benefits)
- ACH transfers (bill payments, peer-to-peer transfers)
- Wire transfers within the U.S.
- Check processing
What Is a SWIFT Code?
- Scope: International transactions
- Format: 8–11 characters (letters and numbers, e.g., NRTHUS33XXX)
- Uses:
- International wire transfers
- Cross-border payments
- Global bank identification
Routing Number vs. Account NumberBanking transactions rely on two critical identifiers: the routing number and the account number. While they often appear together on checks or in online banking, they serve very different purposes. Understanding the distinction helps ensure your money is transferred correctly and securely.What Is a Routing Number?A routing number is a nine-digit code that identifies the financial institution where your account is held. It acts like the “address” of your bank in the U.S. payment system.
- Purpose: Directs funds to the correct bank.
- Scope: Used only in the United States.
- Common Uses:
- Direct deposits (payroll, government benefits)
- ACH transfers (bill payments, peer-to-peer transfers)
- Domestic wire transfers
- Check processing
- Example: 031101266
What Is an Account Number?
Every bank account has a unique identifier known as the account number. This number is essential for managing your finances, as it ensures that deposits, withdrawals, and transfers are directed to the correct account. Whether you’re setting up direct deposit, paying bills, or receiving funds, knowing your account number is crucial
- Purpose: Directs funds to the correct account within the bank.
- Scope: Used globally.
- Common Uses:
- Receiving deposits into your account
- Paying bills or making transfers
- Identifying your account for customer service or online banking
- Example: 123456789012
Read also:How to improve your credit score
Where to Find Your Account Number and Routing Number
When setting up direct deposits, paying bills, or transferring money, you’ll often be asked for two key identifiers: your account number and your routing number. These numbers work together to ensure that funds are directed to the right bank and the right account. Knowing where to find them can save you time and prevent costly errors.
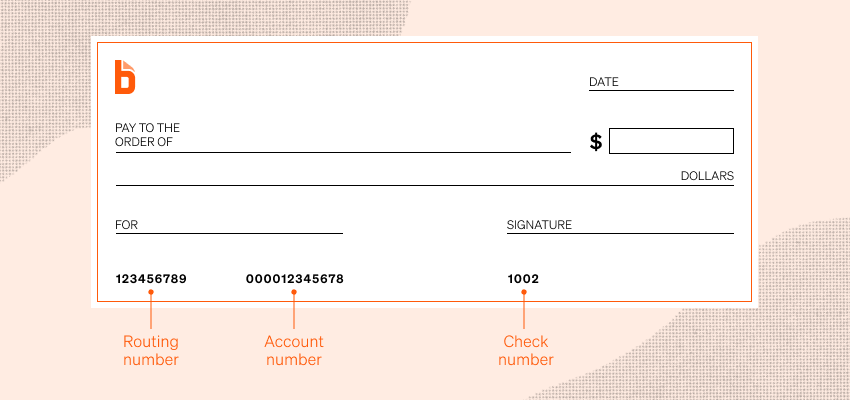
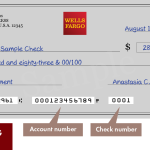
1. On a Check
At the bottom of a paper check, you’ll see three sets of numbers printed in magnetic ink:
- Routing number: First nine digits on the left.
- Account number: Immediately to the right of the routing number.
- Check number: Appears on the far right and also at the top right corner of the check.
2. Online Banking or Mobile App
- Log in to your bank’s online portal or mobile app.
- Navigate to Account Details or Account Information.
- Both numbers are usually listed there.
3. Bank Statements
- Your account number is often displayed in the account summary section.
- Some banks also include the routing number on statements.
4. Customer Service
- Call your bank or visit a branch.
- A representative can provide your routing number and account number securely.
- How Does Zelle Work? Send And Receive Money - February 16, 2026
- The difference between Checking and Savings Accounts - February 16, 2026
- How to track financial metrics in business - February 13, 2026